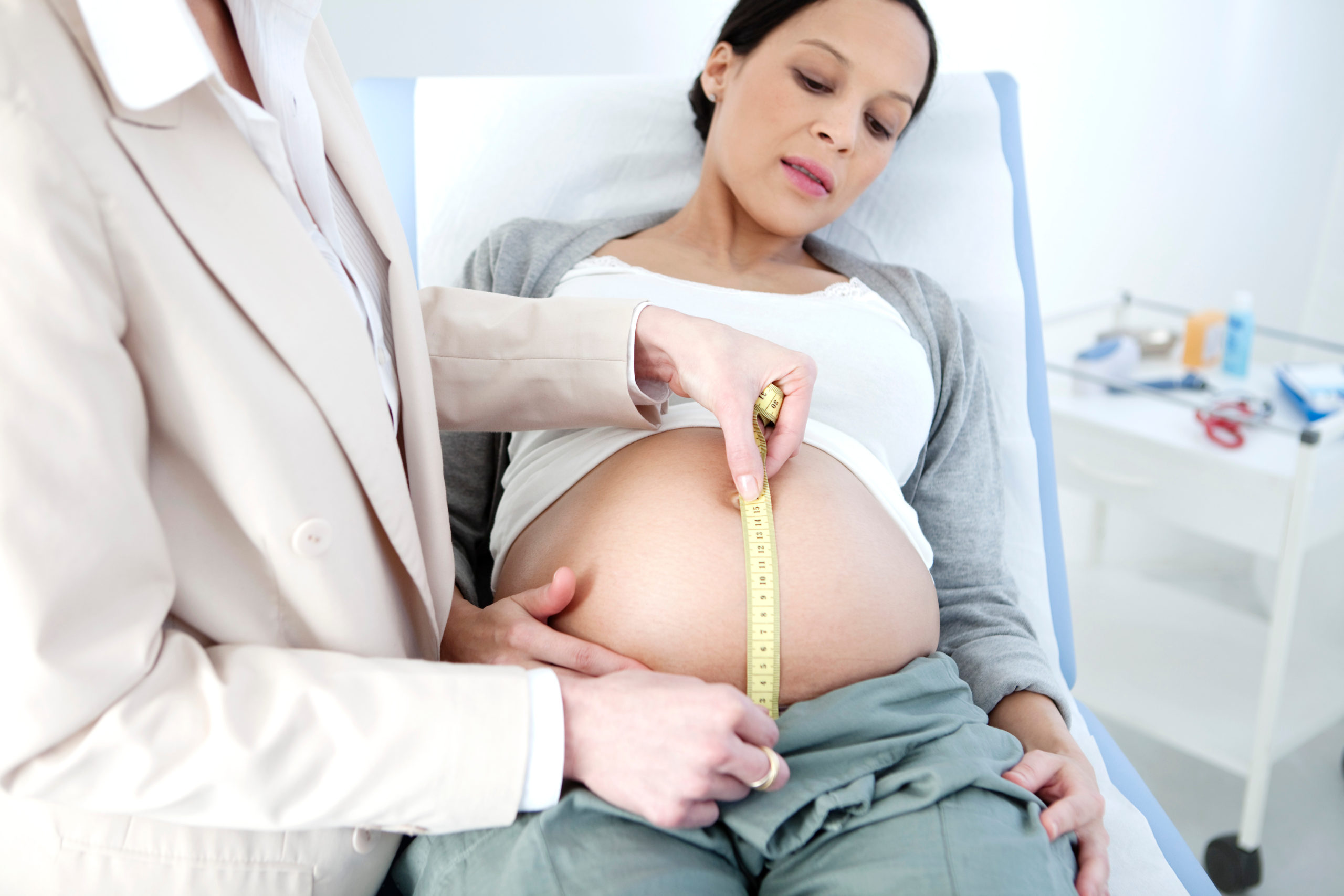
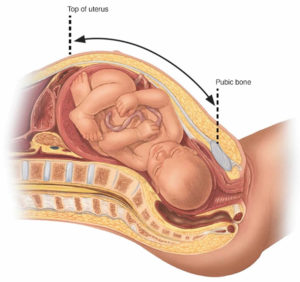
A fundal height measurement is generally defined as the distance in centimeters from the pubic bone to the top of the uterus. The expectation is that after week 24 of pregnancy, the fundal height for a normally growing baby will match the number of weeks of pregnancy — plus or minus 2 centimeters. For example, if you’re 27 weeks pregnant , your health care provider would expect your fundal height to be about 27 centimeters.
What does a fundal height measurement tell us?
Fundal height measurements can be used to determine if a baby is small for its gestational age . If the measurement is significantly smaller than what is expected, it may indicate that the baby is not growing properly and may need further evaluation.
For example, if you’re 27 weeks pregnant, your health care provider would expect your fundal height to be about 27 centimeters. If it’s significantly less than that, it could indicate a problem with the baby’s growth.
How the fundal height is measured?
To take a fundal height measurement, your health care provider will simply measure the distance from your pubic bone to the top of your uterus. A tape measure is used to check the distance between these areas and record the measurement in centimeters (cm).
The zero marker is placed at your pubic bone, and the tape measure is pulled up to the top of your uterus. This is your fundal height measurement. This measurement can be done at each prenatal visit starting around week 24 of pregnancy.
When a tape measure is unavailable, finger widths are used to estimate centimeter (week) distances from a corresponding anatomical landmark.
What can affect the fundal height measurement?
There are a few things that can affect the fundal height measurement:
- The position of your baby during the measurement (babies tend to move around a lot!)
- The amount of amniotic fluid surrounding your baby
- Your abdominal muscle tone (if you have very toned abs, it may be harder to get an accurate measurement)
- Whether you are carrying twins or multiples
What is a normal fundal height?
As your pregnancy progresses, your fundal height measurement will change. The fundus is the uppermost part of the uterus, and during pregnancy, it grows as the baby develops.
At 12 weeks, the fundus is at the level of the pubic bone. By 16 weeks, it’s usually halfway between the pubic bone and the belly button (the umbilicus). By 20 weeks, it typically reaches the belly button. After 24 weeks, the measurement in centimeters should match (within a centimeter or two in each direction) the gestational age of your baby. So if you’re 25 weeks pregnant, your fundal height should be about 23 to 27 centimeters. After 36 weeks, the fundal height may decrease as the baby engages in your pelvis (moves down) in preparation for labor.
In the later stages of pregnancy, the fundal height may decrease as the baby engages in your pelvis (moves down) in preparation for labor. About an hour after delivery, your uterus will go down to where it was at 20 weeks (around your belly button).
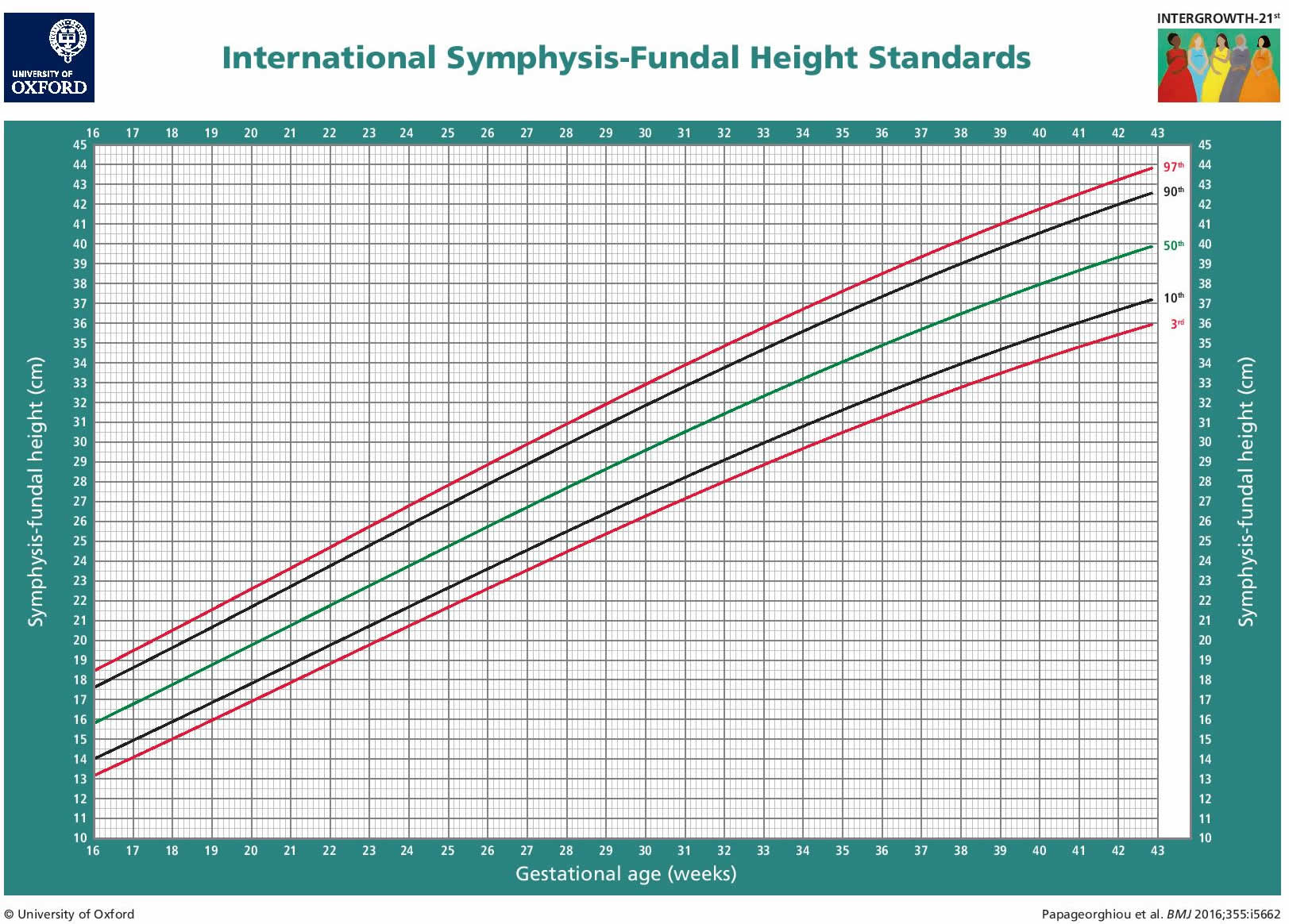
What can cause a small fundal height measurement?
There are many possible causes of a small fundal height measurement, including:
- Pregnancy complications such as preeclampsia or gestational diabetes
- Poor nutrition
- Infection
- Abnormalities of the uterus or cervix
- Certain medications such as steroids
- Smoking
If you have a small fundal height measurement, your health care provider will likely order further testing to determine the cause. This may include an ultrasound or other imaging tests, as well as blood tests.
Treatment for a small fundal height will depend on the underlying cause. If the cause is a pregnancy complication, treatment may involve close monitoring of the pregnancy and/or delivery by cesarean section. If the cause is poor nutrition, your health care provider may recommend changes to your diet.
What can cause a large fundal height measurement?
There are several possible causes of a large fundal height measurement, including:
- Multiple gestation ( twins or triplets)
- Hydramnios (too much amniotic fluid)
- Macrosomia (a large baby)
- Obesity
If you have a large fundal height measurement, your health care provider will likely order further testing to determine the cause.
Detecting abnormal fetal growth
As any expectant parent knows, the health of their unborn child is of the utmost importance. One way to gauge the well-being of a fetus is to track its growth. Fetal size, as defined by estimated fetal weight, is a good indicator of overall health. A fetus is considered small if it falls below the 10th percentile for its gestational age, and large if it is above the 90th percentile. If a fetus falls within these limits, its size is considered appropriate for its gestational age. Tracking fetal growth can therefore give doctors and parents valuable information about the health of the fetus. In addition to monitoring for appropriate growth, doctors also look for signs of abnormalities such as macrosomia (abnormally large size) or microcephaly (abnormally small head). By keeping an eye on fetal growth, doctors can ensure that fetuses are developing normally and flag any potential problems.
Why is important to know my gestacional age?
Determining the gestational age of a fetus is an important part of prenatal care. Accurate dating is essential for assessing the risk of preterm labor and delivery, as well as for determining the appropriate timing and course of other interventions, such as antenatal testing and induction of labor. There are two primary methods for estimating gestational age: using the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP) or using ultrasound. Your doctor will likely use both methods to get the most accurate estimate. The LMP method is based on the principle that ovulation occurs approximately 14 days after the start of the last menstrual period. This method is only reliable, however, if you have a regular menstrual cycle. If your cycles are irregular, your doctor may instead rely on ultrasound to estimate gestational age. Ultrasound dating is based on measurements of fetal structures, such as the length of the femur (thigh bone), and can be performed as early as 10-12 weeks into pregnancy. Gestational age estimation is an inexact science, but it is an important tool for ensuring a healthy pregnancy.
What are the risks of fundal height measurements?
There are no risks associated with having a fundal height measurement. Your healthcare provider will measure your fundal height at each prenatal consultation after 24 weeks.



